In today’s globalized economy, the world has become more interconnected than ever before. This interconnectedness presents businesses with both opportunities and challenges, particularly when it comes to financial transactions. Whether you are a freelancer collaborating with clients across continents or a multinational company sourcing products from different corners of the globe, the ability to handle payments in multiple currencies is no longer just a convenience—it’s an absolute necessity. This need for seamless international transactions is where multi-currency invoicing becomes a key tool for modern businesses.
As the business world continues to expand beyond national borders, the demand for multi-currency invoicing is growing rapidly. In a global marketplace, ensuring financial transparency and accuracy is essential. Clients expect to receive invoices in their local currency to avoid confusion and ensure clarity in the transaction. For businesses, this not only helps maintain client satisfaction but also accelerates the payment cycle, reducing the risks of payment delays. For example, a company in the United States working with clients in Europe or Asia will need to offer invoices in euros or yen, respectively, to make the payment process easier and more efficient for the client.
However, multi-currency invoicing comes with its set of challenges. One of the most prominent issues businesses face is fluctuating exchange rates. The exchange rate between two currencies can change quickly, and this fluctuation can have a significant impact on the amount that a business ultimately receives. This becomes especially problematic when payment is delayed or if there is a significant gap between the issuance of the invoice and when the payment is made. Additionally, currency conversion fees can eat into profits, with international banks and payment gateways often charging a percentage for converting currencies.
Tax regulations add another layer of complexity to multi-currency invoicing. Different countries have varying tax structures and regulations, and businesses must comply with the specific tax rules of both their home country and the client’s country. For instance, a business invoicing a European client must factor in VAT (Value Added Tax), while a business in the U.S. may need to account for sales tax or other regional tax requirements. Ensuring compliance with these regulations can be time-consuming and requires a thorough understanding of tax law in both the business’s and the client’s jurisdiction.
Moreover, businesses must also be mindful of the local invoicing practices in each country. In some regions, additional information or documentation may be required, such as a breakdown of the VAT or a reference number that is mandatory for processing payments. Missteps in meeting these local requirements could result in delayed payments or, even worse, non-compliance penalties.
To navigate these complexities effectively, businesses need a streamlined solution that automates the invoicing process. A robust invoicing system can adjust for exchange rate fluctuations, support multiple currencies, and ensure that all local tax laws are followed correctly. Such a system can handle the heavy lifting, reducing the burden on finance teams and minimizing the risk of errors in the invoicing process. This not only ensures that businesses stay compliant with international laws but also helps maintain positive relationships with clients by providing accurate, transparent, and easy-to-understand invoices.
Furthermore, managing multi-currency invoices manually can be prone to human error. Simple mistakes, such as incorrectly converting a currency or missing a tax code, can cause significant delays and result in strained client relationships. With automation, businesses can generate invoices in multiple currencies with precision, providing clients with accurate details about the amount owed, including exchange rates used and the total converted amount. This level of transparency not only fosters trust but also makes the payment process much more straightforward for international clients.
In summary, the increasing globalization of businesses necessitates the use of multi-currency invoicing to ensure smooth, transparent, and efficient financial transactions. While there are challenges such as currency fluctuations, conversion fees, and complex tax regulations, adopting a well-equipped invoicing system can help businesses manage these issues effectively. By automating the invoicing process, businesses can offer seamless and compliant transactions across multiple currencies, enhancing customer satisfaction and facilitating faster payments. This will ultimately enable businesses to remain competitive in a global market while minimizing financial risks.
Understanding the Basics of Multi-Currency Invoicing
A multi-currency invoice is an invoicing document that is issued in a currency different from the seller’s base or standard currency. This type of invoice is crucial for businesses that operate on a global scale, as it facilitates smoother transactions by allowing clients to pay in their preferred currency. Businesses that provide international services, ship products abroad, or manage teams and operations across various regions must often deal with cross-border payments. Multi-currency invoicing streamlines this process, making it easier for businesses to manage and track payments, while also ensuring that clients are billed in the most convenient and accurate manner.
For businesses, multi-currency invoicing offers numerous advantages, not the least of which is improving client satisfaction. Clients prefer to receive invoices in their local currency because it eliminates the need for them to calculate conversion rates, which can sometimes be an inconvenient and error-prone process. By billing clients in their currency, businesses foster a more transparent relationship and reduce the chance of misunderstandings, late payments, or disputes over currency conversion. Furthermore, issuing invoices in multiple currencies helps businesses maintain a competitive edge in the global market, as it aligns with the expectations of international clients and partners.
The core components of a multi-currency invoice go beyond just the invoice amount. It includes several distinct elements, such as the currency symbol, the amount in the selected currency, the exchange rate used for conversion, and the date the rate was applied. For example, if a company based in the United States needs to issue an invoice to a client in the European Union, the invoice must display the amount in euros (EUR) rather than dollars (USD). The exchange rate that was applied to convert the amount from USD to EUR should also be included on the invoice, along with the specific date on which that exchange rate was valid. This extra information not only aids in the payment process but also ensures that both parties understand the true value of the transaction, considering fluctuating exchange rates. Including the exchange rate on the invoice is especially important if there is a delay between the issuance of the invoice and the actual payment, as currency rates can vary significantly during that time.
Additionally, multi-currency invoicing involves adhering to local tax laws and regulations, which can differ greatly from one country to another. Different regions have unique rules regarding how taxes should be handled on international invoices. For example, in the European Union, Value Added Tax (VAT) must be displayed on invoices, even if the transaction is in a currency outside the EU. The tax calculation becomes even more complex if the business is dealing with a client located in a non-EU country, as VAT rules may differ depending on the country. Similarly, in countries like Canada, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) or Harmonized Sales Tax (HST) may need to be converted into the equivalent amount in the business’s base currency, such as Canadian dollars (CAD).
Given the complexity of handling taxes and exchange rates across different regions, manually managing these factors can be tedious and prone to mistakes. Businesses that rely on manual systems for invoicing risk errors in calculations, which could lead to financial losses or regulatory issues. For instance, failing to apply the correct tax rate or currency conversion could result in non-compliance with local tax laws, which could expose the business to legal penalties. Inaccurate invoices can also damage relationships with clients if they feel that the process is not transparent or that the amounts are incorrect.
Fortunately, automated invoicing tools simplify this process, offering businesses the ability to handle multi-currency transactions efficiently and accurately. These tools are designed to automatically adjust exchange rates and ensure that all legal and tax requirements are met, eliminating the need for manual calculations. Automated invoicing systems also present invoices in a professional format, ensuring consistency and compliance with international invoicing standards. These tools not only streamline the invoicing process but also reduce the risk of errors, allowing businesses to focus more on growth and client relations instead of dealing with complex financial paperwork. With the right tools in place, businesses can easily manage cross-border payments, avoid potential pitfalls in international invoicing, and ultimately enhance their global operations.
In conclusion, multi-currency invoicing is an indispensable feature for businesses that operate internationally. By issuing invoices in the client’s preferred currency, businesses can simplify transactions, enhance client satisfaction, and avoid unnecessary fees or delays. However, ensuring accuracy in currency conversions, applying the correct exchange rates, and complying with local tax laws requires careful attention to detail. Automation tools can significantly ease this process, providing businesses with the precision and professionalism needed to handle global transactions efficiently while minimizing the risk of errors and compliance issues.
Identifying When to Use Multi-Currency Invoices
In today’s interconnected world, businesses must carefully assess when to issue multi-currency invoices to optimize both operational efficiency and client satisfaction. As globalization continues to blur national borders, businesses increasingly interact with clients from diverse regions, and the need for multi-currency invoicing has become indispensable. Whether your company deals with international clients on a regular basis, operates on global online platforms, or you are a freelancer working with clients from various countries, using multi-currency invoices is no longer just a convenience—it is essential for smooth transactions.
Clients appreciate being billed in their local currency for a number of reasons. For one, it simplifies their financial records, as they do not have to deal with exchange rate conversions or surprise conversion fees that could otherwise cause confusion or unexpected expenses. In addition, when a client receives an invoice in their preferred currency, the entire process feels more transparent and manageable, reducing the likelihood of payment delays or disputes. For instance, if a graphic designer in the United States works with a client based in the United Kingdom, issuing an invoice in GBP (British Pounds) not only enhances clarity but also streamlines the payment process, as the client does not have to contend with currency exchange or additional fees.
The decision to bill in the client’s currency or your own is one that requires careful consideration. There are several advantages to invoicing in the client’s local currency. For one, it improves client satisfaction by making the payment process easier and more transparent. When clients are billed in their native currency, there is less friction when it comes time to make payment, as they don’t have to deal with conversion fees or worry about exchange rate discrepancies. This can also lead to quicker payments, as the transaction feels more straightforward from the client’s perspective. Additionally, it shows a level of professionalism and attentiveness to the client’s needs, which can strengthen the business relationship.
However, invoicing in the client’s currency comes with some risks, particularly due to the volatility of exchange rates. Currency exchange rates fluctuate regularly, and the value of a currency can change significantly between the time the invoice is issued and the time payment is made. If the exchange rate moves unfavorably, the amount received in your currency could be substantially less than originally anticipated. For businesses with tight profit margins, this can create financial uncertainty and impact cash flow. This unpredictability is a risk that businesses must weigh carefully, especially in markets where exchange rate fluctuations are frequent or severe.
On the other hand, invoicing in your own currency offers its own set of benefits and drawbacks. The primary advantage of billing in your currency is that it shields your business from exchange rate volatility. By avoiding currency fluctuations, you can ensure more stable and predictable revenue, as you will know exactly how much you will receive in your base currency. This is particularly important for businesses that need to maintain accurate financial projections and avoid surprises in revenue. Additionally, invoicing in your own currency simplifies the accounting process, as there are fewer variables to track and no need for conversion calculations.
However, billing in your own currency can lead to complications for the client, which may affect the overall business relationship. Clients may face additional costs related to currency conversion, or they may experience delays as they handle the conversion process through their own bank or financial institution. These extra steps can introduce frustration and reduce the ease of doing business, which may result in longer payment cycles or, in some cases, payment disputes. For businesses looking to foster positive relationships and encourage repeat clients, invoicing in the client’s currency can often be a more customer-centric choice.
The decision between billing in the client’s currency or your own largely depends on the nature of the client relationship, the currency volatility in the region, and your internal financial systems. For long-term projects or contracts in countries with stable and predictable currencies, billing in the client’s local currency can foster trust and efficiency, making it easier to manage the payment process. Conversely, for short-term projects, transactions in regions where the currency is prone to significant fluctuations, or where the cost of conversion is high, invoicing in your own currency may be the safer and more predictable option.
Moreover, businesses can tailor their invoicing strategy based on the nature of the client relationship. For instance, for high-value, long-term contracts with international clients, the benefits of invoicing in the client’s currency typically outweigh the risks, as the business relationship is likely to be strong enough to absorb occasional fluctuations in exchange rates. However, for smaller, one-off transactions or when dealing with currencies that exhibit erratic fluctuations, businesses might opt to issue invoices in their own currency to minimize risk.
In conclusion, understanding when to use multi-currency invoices is crucial for maximizing client satisfaction and optimizing business operations. While invoicing in the client’s currency can enhance convenience and professionalism, it also exposes businesses to exchange rate risks. Conversely, billing in your own currency can simplify accounting and provide financial predictability, but it may lead to inconveniences for clients. By weighing these factors carefully and aligning invoicing practices with the client’s location and the nature of the transaction, businesses can ensure smoother international operations and stronger, more reliable client relationships.
Choosing the Right Currency: Business Strategy & Client Preference
Managing multi-currency invoicing requires a delicate balance between protecting your business from currency risk and ensuring client satisfaction. With the globalization of trade, offering invoices in a client’s preferred currency has become not just a convenience, but an expectation. When billing in the client’s currency, businesses can enhance the customer experience by eliminating unexpected conversion fees and providing greater transparency. This approach often increases trust and minimizes friction in the payment process, which is crucial for maintaining smooth business relationships. However, despite the benefits, this method also exposes businesses to the volatility of currency fluctuations, a risk that can severely affect profitability, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) where even slight shifts in exchange rates can have significant financial consequences.
The key to managing this risk is in deciding whether to fix the exchange rate in your contracts or allow it to fluctuate. Fixing the exchange rate is a common approach used by businesses engaging in long-term contracts or ongoing projects, where the pricing structure remains the same over a period of time. By locking in a specific exchange rate at the time the agreement is made, both parties know exactly what to expect financially, ensuring predictable payments. This strategy brings stability and minimizes the financial uncertainty associated with currency exchange rate fluctuations. However, this approach requires diligent monitoring of exchange rates and may necessitate adding a buffer into the pricing structure to account for potential future shifts in the market. This buffer acts as a safeguard, protecting the business from sudden changes in currency values that could erode profits.
On the other hand, allowing exchange rates to fluctuate with the market conditions offers a more flexible approach to invoicing. This method is particularly useful for businesses engaged in one-off transactions or short-term projects where exchange rates are relatively stable, or the cost of exchange fluctuations is minimal. By allowing rates to adjust according to market conditions, businesses can ensure that invoices accurately reflect the true value of services or products in real-time. This adaptability can be advantageous for businesses operating in regions with currencies that are subject to significant volatility, as it allows them to adjust prices in response to the market. However, while this flexibility can be beneficial, it also introduces an element of unpredictability, where businesses may experience unexpected gains or losses based on the fluctuating exchange rates. For example, if a currency strengthens after an invoice is issued; the business could end up receiving less than expected when the payment is made.
The ability to manage exchange rate risks also involves clearly defining currency terms during the initial stages of the client relationship. When negotiating the terms of any agreement, it’s essential to be transparent about which currency will be used for invoicing and whether exchange rates will be fixed or allowed to fluctuate. This clarity helps set the right expectations and prevents any confusion down the line. For instance, offering clients the option to pay in their local currency with an additional margin or in your own currency with no added fees provides them with more control over how they prefer to handle payments. This flexibility can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, as it gives clients the choice to avoid conversion fees or the potential complications of dealing with exchange rate fluctuations.
Being transparent about your pricing and invoicing practices also helps build trust with international clients. A clear understanding of the currency terms allows parties to plan accordingly, avoiding surprises and disputes related to payments. For businesses, offering the option to bill in the client’s currency can strengthen the relationship and create goodwill. It shows a level of consideration for the client’s needs, making it easier for them to process payments, which in turn can lead to faster settlement of invoices. Conversely, invoicing in the business’s own currency could be perceived as more advantageous for the company, but it may be less appealing to clients if it results in additional charges or payment delays.
Another important consideration in the decision-making process understands the client’s location and the stability of the currency in their region. For example, in countries where the currency is highly volatile, it may be wise to offer clients the option to pay in your own currency to avoid the risk of large fluctuations. For more stable markets, where exchange rates remain relatively constant, offering the option to invoice in the client’s currency could be more beneficial. Additionally, businesses should assess the potential impact on their accounting and financial systems when managing multiple currencies. Effective currency management not only enhances client satisfaction but also streamlines internal accounting processes, ensuring that invoicing, payments, and financial reporting are handled accurately and efficiently.
In conclusion, choosing the right currency for invoicing is a strategic decision that requires careful thought and consideration of multiple factors, including currency volatility, client preferences, and long-term financial goals. By managing exchange rate risk and maintaining flexibility in currency selection, businesses can strike the right balance between protecting their financial interests and fostering positive relationships with international clients. Through careful negotiation and clear communication, businesses can enhance their invoicing processes, minimize risks, and ensure smoother, more transparent transactions with clients around the world.
Dealing with Exchange Rates: Clarity, Accuracy & Updates
One of the most crucial aspects of multi-currency invoicing is how businesses handle exchange rates. Deciding whether to use real-time exchange rates or a fixed rate for invoicing is a critical decision that can affect both the accuracy and transparency of the invoicing process. Exchange rate management requires careful planning to ensure that businesses are not exposed to unnecessary risks while maintaining clear communication with clients. The method chosen depends largely on the nature of the transaction, the frequency of invoicing, and the financial goals of the business.
Real-time exchange rates are used to reflect the market value of the currency at the time the invoice is issued. This approach provides the most up-to-date accuracy, ensuring that the client is charged the current value of the transaction based on the most recent market rates. Real-time rates are ideal for businesses that issue frequent invoices, such as those operating in industries with fast-paced, dynamic pricing models or for companies with relatively moderate transaction values. This method is highly flexible and allows businesses to align their invoicing with the ever-changing market conditions. It also ensures that the business is receiving the correct amount based on the latest currency values, making it a preferred choice for companies looking to stay on top of currency fluctuations and adjust their pricing accordingly.
However, real-time exchange rates also come with certain risks. The value of currencies can fluctuate significantly in a short period, and these fluctuations can impact both the business’s revenue and the client’s payment. When exchange rates change suddenly between the time the invoice is issued and the payment is made, businesses may find that the amount they receive is considerably different from the original value. For example, if a company invoices a client in euros but the exchange rate weakens between the issue and payment dates, the business may end up with less value when the payment is converted back into its base currency. While this method provides the most accuracy, it requires continuous monitoring of currency trends and can create financial uncertainty, especially for smaller businesses that may not have the resources to manage such volatility.
Alternatively, businesses may choose to use a fixed exchange rate for the duration of a project or billing period. This method helps to create more predictable financial outcomes by locking in a set exchange rate at the time the invoice is issued. By using a fixed rate, businesses and clients can better forecast the cost of a transaction and establish a clearer financial plan. This approach is particularly useful for long-term contracts or recurring projects, where both parties would prefer the stability of knowing exactly how much will be paid and received, regardless of market movements.
While fixed exchange rates offer predictability, they can also come with certain drawbacks. To account for the possibility of fluctuations in the currency value during the invoicing cycle, businesses often add a buffer to the fixed exchange rate. This buffer ensures that if the currency moves unfavorably, the business won’t lose out on too much revenue. On the other hand, if the currency strengthens, the business might end up receiving more than originally anticipated. While this flexibility can be beneficial in some situations, it also introduces a level of uncertainty for both parties. Businesses must decide how much of a buffer to add, and striking the right balance is essential to avoid potential disputes.
Regardless of whether real-time or fixed exchange rates are chosen, clarity is key in the invoicing process. It is essential to provide full transparency by showing exchange rate details clearly on the invoice. Clients should be able to see the original currency amount, the exchange rate that was applied, and the converted amount. By providing this level of detail, businesses can avoid confusion or disputes that may arise due to market fluctuations. Transparency builds trust between businesses and clients, assuring them that the invoicing process is fair and accurate. This openness also ensures that clients feel confident in the process, even when exchange rates fluctuate, as they can see exactly how the final amount was calculated.
In addition to providing the exchange rate details, it’s crucial for businesses to include the date on which the exchange rate was applied. This date helps to establish a reference point, especially in cases where there are significant changes in the currency market. By clearly indicating when the rate was set, businesses can protect themselves from potential disputes that may arise if the client questions the fairness of the conversion.
Managing exchange rates with clarity, accuracy, and transparency ensures that multi-currency invoicing is smooth and efficient for both businesses and their clients. Regardless of the method chosen, providing detailed breakdowns of the exchange rates used fosters trust, minimizes potential misunderstandings, and ensures that both parties are on the same page when it comes to billing. With the right approach, businesses can navigate the complexities of multi-currency invoicing while maintaining strong, transparent relationships with their international clients.
Structuring a Multi-Currency Invoice: Best Practices
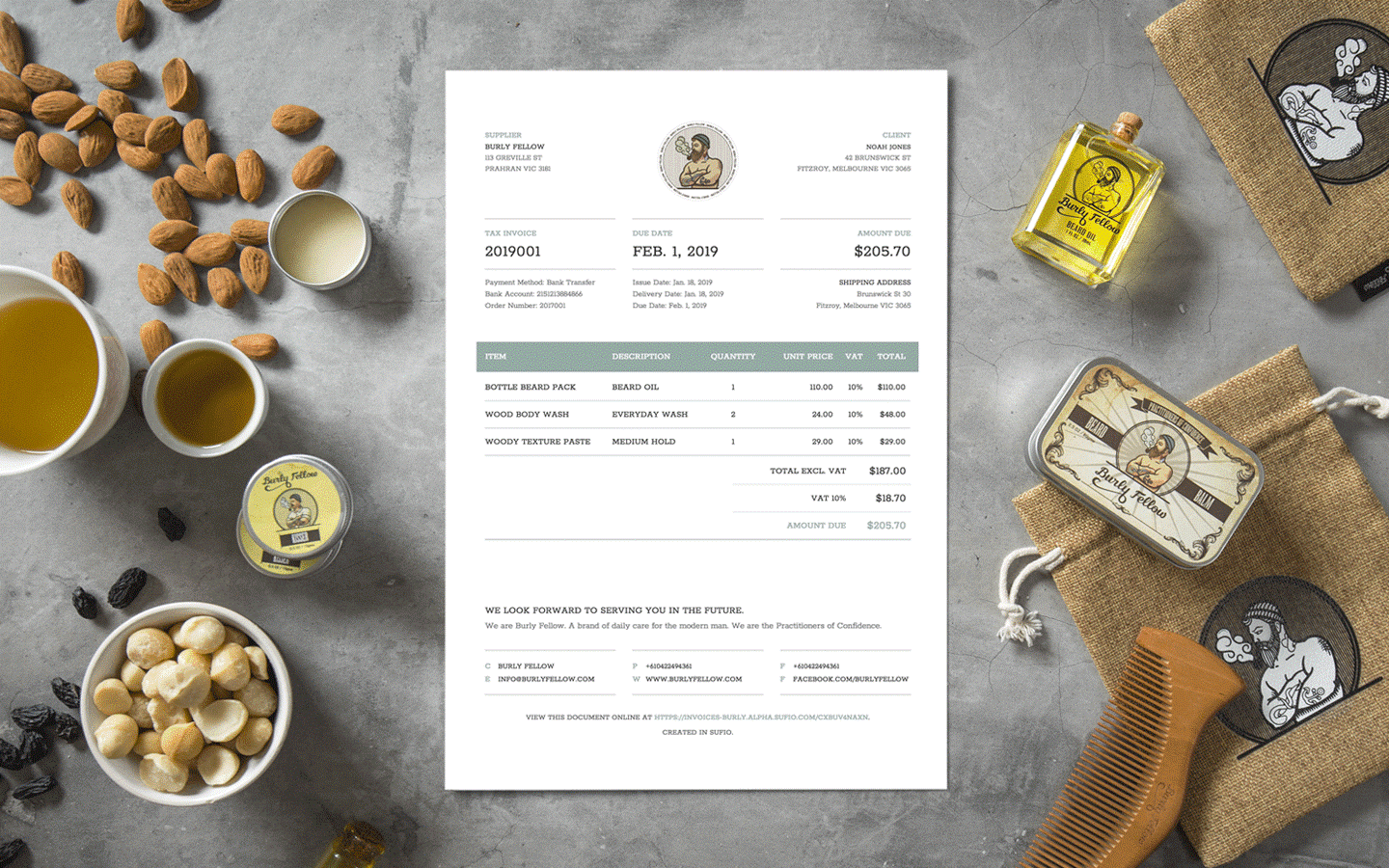
When structuring a multi-currency invoice, clarity, and compliance are of the utmost importance to ensure smooth transactions and maintain a professional appearance. A well-structured invoice not only ensures accurate payment but also fosters trust with clients by providing transparency and reducing the chances of disputes. One of the first elements that should be highlighted on a multi-currency invoice is the title, which should clearly state that the invoice is in multiple currencies. This helps clients quickly understand the nature of the transaction and avoids any confusion regarding the amounts being billed.
For businesses invoicing in different currencies, it is essential to display both the original and converted amounts clearly. For example, if a business is pricing a product or service in USD but issuing the invoice in EUR, the invoice must clearly show both amounts—USD and EUR—along with the exchange rate that was used to make the conversion. Additionally, including the date on which the exchange rate was applied helps ensure that the transaction remains transparent, especially in cases where exchange rates fluctuate over time. This detailed breakdown ensures that the client understands how the converted value was calculated and can confirm its accuracy, thus reducing the risk of disputes.
Another crucial element of a well-structured multi-currency invoice is the proper handling of local taxes, such as VAT or GST. Different countries have varying tax rules, so it is important to apply the correct tax rates based on the client’s location. The invoice should clearly separate the pre-tax subtotal, applicable taxes, and the final payable amount. By clearly breaking down these sections, businesses not only comply with local tax laws but also ensure that the client is aware of exactly how the taxes were calculated, minimizing confusion.
Moreover, including disclaimers in the footer of the invoice adds an extra layer of transparency. These disclaimers can mention how the exchange rate was derived, which sources were used, and whether there are any potential bank charges or fees involved in the transaction. This level of detail provides assurance to clients, ensuring that they understand the full scope of the billing process and any additional costs that may apply. By adhering to these best practices, businesses can ensure that their multi-currency invoices are clear, accurate, and compliant with local regulations, making the payment process smoother for both parties.
Taxation and Compliance for Cross-Border Invoicing
Cross-border invoicing presents businesses with the challenge of navigating intricate and varied tax codes across different regions. These tax rules can differ widely from one country to another, and businesses must ensure they are applying the correct tax rates based on their client’s location and tax registration status. For instance, in the European Union, businesses that are VAT-registered must adhere to the Value Added Tax regulations, while in countries like Canada and Australia, Goods and Services Tax (GST) is the applicable tax system. Understanding these complex tax frameworks is essential for avoiding errors and ensuring full compliance.
One key concept businesses must be aware of in cross-border invoicing is the reverse charge mechanism, particularly in the EU. This rule applies when both the buyer and seller are VAT-registered businesses. In this case, VAT is not charged by the seller but is instead self-reported by the buyer. This mechanism helps streamline cross-border transactions within the EU but can create confusion if not correctly applied. Businesses must confirm the VAT registration status of their clients and ensure they are following the appropriate procedures for reverse charge transactions.
To ensure compliance, businesses should always gather their clients’ tax identification numbers (tax IDs) and verify whether taxes should be included or excluded on the invoice. Displaying the tax percentage applied on the invoice, along with the client’s tax ID, is a critical part of meeting both local and international tax regulations. This ensures transparency and makes it easier for the client to verify the tax calculation, especially if they are located in a jurisdiction with different tax laws.
Furthermore, businesses engaged in cross-border invoicing must familiarize themselves with international tax treaties that can prevent double taxation. Double taxation occurs when both the client’s and the business’s home countries impose taxes on the same transaction, potentially leading to inflated costs for the client and reduced profits for the business. By researching the relevant tax treaties between the countries involved, businesses can minimize the risk of double taxation and ensure that only one tax is applied to the transaction. Understanding these treaties is crucial for international businesses, as it helps streamline invoicing and fosters stronger relationships by reducing the client’s financial burden.
Maintaining compliance with cross-border tax laws requires diligence, research, and an understanding of both local and international tax frameworks. By ensuring that the correct tax rates are applied and that the necessary documentation is included on the invoice, businesses can mitigate risks associated with tax issues and create a more efficient invoicing process. In turn, this not only ensures legal compliance but also builds trust with clients, encouraging smoother business transactions and fostering long-term relationships.
Payment Gateways & Receiving Foreign Payments
Choosing the right payment gateway is a crucial aspect of managing international payments effectively. The choice of payment gateway can significantly impact transaction costs, processing times, and overall ease of use, particularly when dealing with foreign clients. Different platforms, such as PayPal, Stripe, Wise, and traditional bank transfers, come with unique benefits and challenges, and businesses must assess which option aligns best with their needs.
PayPal is one of the most popular and widely accepted payment gateways globally. Its convenience and familiarity to customers make it an attractive option for businesses dealing with international clients. However, while PayPal offers ease of use and fast processing times, it often comes with higher transaction fees compared to other platforms. These fees can add up quickly, particularly for smaller transactions, and reduce overall profitability. This makes PayPal a better option for businesses with lower transaction volumes or those looking for simplicity and widespread recognition.
Stripe, on the other hand, provides a more customizable solution that integrates seamlessly with invoicing systems and offers a higher level of flexibility in terms of payment processing. Stripe’s ability to support various payment methods and its integration with online platforms make it ideal for e-commerce businesses. While it may not have the same global acceptance as PayPal, it provides a more robust solution for businesses seeking to streamline their payment processing and expand their capabilities.
Wise (formerly TransferWise) stands out in the multi-currency landscape due to its low conversion fees and real exchange rates. It offers businesses the ability to send and receive payments across borders at competitive rates, significantly reducing the costs associated with currency conversions. For companies that frequently deal with international payments and need to minimize fees, Wise provides a cost-effective solution. Additionally, its transparent fee structure and fast processing times make it an appealing choice for businesses looking to enhance operational efficiency.
For larger transactions, traditional bank transfers are often the preferred method. While they provide a secure and reliable way to transfer large sums, they tend to be slower and come with higher fees, especially when dealing with international payments. These transactions may take several days to process, and some banks may impose additional charges for currency conversion and international transfers. However, for businesses involved in high-value transactions or long-term contracts, direct bank transfers offer a secure and trusted payment method.
A key consideration when dealing with foreign payments is minimizing currency conversion fees. Exchange rate fluctuations and high conversion fees can quickly erode profits, especially for businesses that regularly handle cross-border transactions. Platforms like Wise, which offer low conversion fees and real exchange rates, help businesses keep costs under control. Additionally, negotiating better rates with banks and payment providers can further reduce the financial impact of currency conversion.
Automating payment tracking and reconciliation across multiple currencies is another vital aspect of managing international payments efficiently. By using automated tools, businesses can streamline the process of tracking payments, ensuring that all incoming and outgoing transactions are recorded accurately. Automation reduces human error, saves time, and helps businesses maintain a clear financial overview. This process also ensures that businesses stay on top of outstanding invoices and payment deadlines, improving cash flow management and minimizing the risk of missed or delayed payments.
In conclusion, selecting the right payment gateway and minimizing currency conversion fees are critical factors in maintaining profitability and efficiency in international transactions. By evaluating the advantages and drawbacks of platforms like PayPal, Stripe, Wise, and traditional bank transfers, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs. Additionally, leveraging automation tools for payment tracking and reconciliation further streamlines the payment process, ensuring that businesses remain competitive in a global marketplace.
Automating Multi-Currency Invoicing
Automating multi-currency invoicing is a game-changer for businesses operating in global markets. By integrating invoicing systems with international accounting software and payment platforms, companies can streamline their invoicing and payment tracking processes. This integration enables businesses to manage cross-border transactions efficiently, reducing the complexity that comes with invoicing in multiple currencies. Automation tools help eliminate the need for manual entry, thereby minimizing human error and saving valuable time. These tools allow businesses to set up pre-defined templates that automatically adjust the currency based on the client’s location and preferences, ensuring that invoices are always accurate and consistent.
With automation, businesses can also apply real-time exchange rates to their invoices. As exchange rates fluctuate regularly, using real-time rates ensures that invoices are calculated based on the most current market values. This reduces the potential for discrepancies between the amount invoiced and the actual amount received, which can often occur when exchange rates change between the issuance of the invoice and the payment date. The system also ensures that the correct conversion rates are applied, so businesses don’t need to manually check or update exchange rates every time they issue an invoice.
Integrating invoicing systems with financial software ensures that these invoicing details sync seamlessly with existing financial records. This integration means that transactions are automatically recorded, providing businesses with up-to-date insights into their revenue and outstanding invoices. It also helps reconcile payments quickly, reducing the administrative workload and improving cash flow management. By automating these processes, businesses can eliminate bottlenecks, ensuring that multi-currency invoices are sent out on time, accurately reflecting the correct amounts, and automatically updated in financial reports.
Overall, automation simplifies the complexities associated with international invoicing by ensuring consistency, accuracy, and real-time synchronization across multiple platforms. This enables businesses to focus on growth and client relationships, while leaving the intricacies of multi-currency invoicing to automated systems.
Conclusion: Scale Globally with Smart, Multi-Currency Invoicing
In today’s fast-paced and interconnected world, businesses aiming for global expansion must ensure that their financial processes are streamlined and efficient. Offering multi-currency invoices is no longer just a luxury but a necessity for businesses that wish to operate seamlessly across borders while maintaining accuracy and building strong client relationships. The ability to issue invoices in multiple currencies allows businesses to cater to clients from different regions, enhancing customer satisfaction and improving overall transaction clarity. This not only boosts the client experience but also mitigates the complexities that come with currency exchange and international payments.
By leveraging the right invoicing tools, businesses can automate the entire process, making currency conversion automatic and ensuring compliance with international tax regulations. This eliminates the need for manual calculations and adjustments, reducing the chances of errors and discrepancies that can lead to disputes or delays. Additionally, businesses can avoid the headaches associated with constantly monitoring fluctuating exchange rates. Automation ensures that the correct rate is applied at the time of invoicing, providing transparency for both the business and the client.
Ensuring tax compliance is another critical aspect of global invoicing. Different countries have different tax rules, and failing to adhere to local tax regulations can result in fines, penalties, and strained business relationships. By automating tax calculations based on the client’s location, businesses can ensure that invoices are compliant with local regulations, reducing the risk of legal issues. Moreover, integrating invoicing systems with financial software ensures that businesses can maintain up-to-date and accurate records without the need for manual input, streamlining the entire process of financial reporting.
When businesses have the right systems in place, they can scale globally with confidence. Multi-currency invoicing removes the financial friction that often accompanies international transactions, enabling businesses to focus on their growth and expansion without being bogged down by complex financial operations. In a world where global competition is fierce, implementing efficient, automated invoicing practices not only ensures smoother transactions but also strengthens relationships with clients, allowing businesses to thrive on the international stage.